Difference between revisions of "Unable to Upgrade Ubuntu"
IVSWikiBlue (talk | contribs) |
IVSWikiBlue (talk | contribs) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
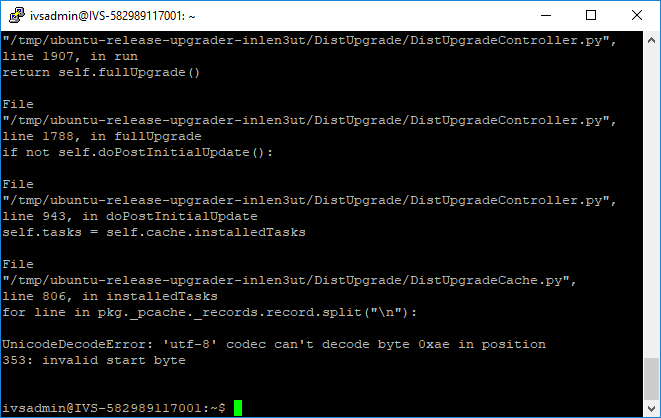
When attempting to update Ubuntu from version 14.04 LTS to 16.04, you may encounter an error when entering the following command: | When attempting to update Ubuntu from version 14.04 LTS to 16.04, you may encounter an error when entering the following command: | ||
:: <pre>do-release-upgrade</pre> | :: <pre>do-release-upgrade</pre> | ||
| − | : | + | :::{{img | file = TS1.png}} |
This error is caused by non UTF-8 characters in the /var/lib/dpkg/status file. Follow the instructions below to identify and remove these characters. | This error is caused by non UTF-8 characters in the /var/lib/dpkg/status file. Follow the instructions below to identify and remove these characters. | ||
# Enter the following command: <pre>grep -avx '.*' /var/lib/dpkg/status</pre> | # Enter the following command: <pre>grep -avx '.*' /var/lib/dpkg/status</pre> | ||
#: This will display any not UTF-8 characters in the file. | #: This will display any not UTF-8 characters in the file. | ||
| − | #: | + | #:{{img | file = TS1.png}} |
# Enter the following command: <pre>sudo nano /var/lib/dpkg/status</pre> | # Enter the following command: <pre>sudo nano /var/lib/dpkg/status</pre> | ||
# Locate the bad characters, and delete them. | # Locate the bad characters, and delete them. | ||
Latest revision as of 14:57, 11 May 2022
UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte
When attempting to update Ubuntu from version 14.04 LTS to 16.04, you may encounter an error when entering the following command:
This error is caused by non UTF-8 characters in the /var/lib/dpkg/status file. Follow the instructions below to identify and remove these characters.
- Enter the following command:
grep -avx '.*' /var/lib/dpkg/status
- Enter the following command:
sudo nano /var/lib/dpkg/status
- Locate the bad characters, and delete them.
- Save the file.
/boot is out of space
- Enter the following command:
dpkg -l | grep linux-image
- This will display all the kernels currently installed. All but the most recent can be safely deleted.
- Enter the following:
apt-get remove ''old-linux-kernel-package-name''
-
Ex: ''apt-get remove linux-image-3.13.0-32-generic''
-